Part 2 of 3;
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
In veterinary practice, type I reactions usually occur, which are realized in stool disorders and atopic (“strange disease” in the Greek language) dermatitis.
Dogs dermatitis
Such dermatitis occurs more often in dogs at the age of 1-3 years, regardless of sex. Dermatitis occurs most often in:
- terriers
- retrievers
- boxers
- spaniels
- German shepherds
- Sharpies
- Dalmatians
- English bulldogs
- Schnauzer
- Setter breed (American Cocker Spaniel, Brittany, Chesapeake Bay Retriever)
- chow
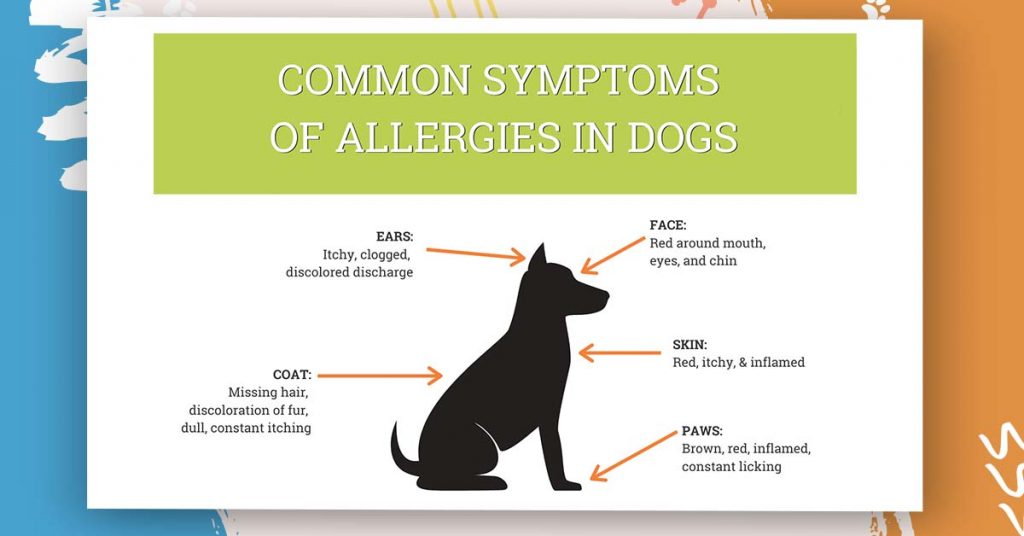
The most typical clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis in dogs are:
- itching
- alopecia
- erythema
- hyperpigmentation
- lichen of the skin (on the muzzle, feet, chest, auricles, abdomen, and tail)
Depending on the type of allergen, atopy may be seasonal, or it may trouble the animal (and its owner) for most of the year.
Cats dermatitis
In cats, the disease occurs in most cases between 6 months and two years of age, regardless of breed or sex. The most common manifestations of dermatitis in cats are itching in the head and neck area, billiard dermatitis, and symmetrical alopecia caused by licking.
However, it is evident that in addition to allergies, several dermatitis and dermatoses are characterized by almost the same, or at least similar, manifestations.
“When You Hear Hooves, Think Horses, Not Zebras”
Theodore Woodward
Genuinely allergic dermatitis
The most common cause of genuinely allergic dermatitis, the least guessed at by pet owners, is not food components but fleas. We have been able to ascertain that, regardless of the complaints of owners who bring their dogs or cats to our clinic, during the warm season, fleas or traces of flea infestation on the animal are found in a large percentage of our patients. Feeding on the animal’s blood, the flea secretes saliva into the dermis, preventing blood from clotting. This saliva contains at least 15 different substances that can have irritating or allergenic effects.
According to the CARLOTTI, D.N.; CASTARGENT, F. Analyse statistique de tests cutanes positifs chez 449 chiens atteints de dermatite allergique “The skin of an nan-allergic dog or cat may not react at all to flea bites”.
The clinical manifestations of allergic flea dermatitis are similar to those described above.
Fleas
Along with fleas in dogs and cats, parasitization of mites (causative agents of demodicosis, heylethiellosis, sarcoidosis) is quite common, and lice are less common. Similar clinical manifestations have parasitizing fungi Malassezia pachydermatous and some dregs.
The similarity of all these diseases is exacerbated because they all manifest as itching. Hence, scratching the itchy skin areas, self-injuring the animal, and layering secondary bacterial dermatitis further spoils the clinical picture.
Therefore, before we talk about the allergic nature of dermatitis, it is necessary to carefully examine the skin and coat of the animal under magnification to exclude the presence of these and other ectoparasites. If the veterinarian identifies parasites, a course of treatment is necessary, with the obligatory recommendation for pet owners to carry out a thorough wet cleaning of the apartment, pet bedding, and the car’s interior.
Food allergens
These factors are much more common than food allergens as a cause of atopy (D.W. Scott et al., 1995). Diagnosis of parasitic lesions, especially helminth infestations, is not always easy. Still, both the doctor and the animal owner should remember that they are not interested in a quick but correct diagnosis. We should not forget the possibility of combined parasitic infestations of several species.
The allergic nature of dermatitis can be discussed only after excluding and eliminating the factors listed above.
These factors are much more common than food allergens as a cause of atopy. Diagnosis of parasitic lesions, especially worm infestation, is not always easy. Still, both the doctor and the pet owner should remember that they are not interested in a quick but correct diagnosis. We should not forget about the possibility of combined parasitic parasites of several species.

Diagnose atopic dermatitis
To diagnose atopic dermatitis in dogs, an animal must have at least three of the following signs:
- itching
- lesions on the muzzle and fingers
- Lichenification on the flexor surface of the hind feet
Treatment of allergic dermatitis must be both locally and systemically targeted. If the disease is complicated by bacterial pyoderma, the primary measure should be eliminating or leveling the bacterial component.
Local treatment should be aimed at suppressing itching. In addition to ointments containing glucocorticoids, it is recommended to use creams or lotions with chamomile extract, local anesthetics, camphor, or menthol.

